- Products
- Services
- Markets
- About
-
 English US
English US
 English US
English US
Chemical Formula: S, HSO4, HSO3, SO4, HS (or S), SO3
Present as: anion
Sulfur or sulphur (see spelling differences) is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16. It is an abundant, multivalent nonmetal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Chemically, sulfur reacts with all elements except for gold, platinum, iridium, nitrogen, tellurium, iodine and the noble gases.
Elemental sulfur occurs naturally as the element (native sulfur), but most commonly occurs in combined forms as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and Egypt. In the Bible, sulfur is called brimstone. Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.
Sulfur is an extremely important non metal but is never use in its elemental form. The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of sulfuric acid for sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, and other chemical processes. The element sulfur is used in matches, insecticides, and fungicides.
Bisulfate is the form of sulfate that exists in very low pH solutions (generally less than pH of 2). Bisulfate, exchanged onto anion resin can hydrolyze off. .
Bisulfite is the monovalent form of sulfite that exists in water at low pH (<5). Bisulfite is removed by strong base anions but throughput capacity is limited by the presence of other anions. Sulfate is the fully oxidized oxo anion of sulfur. It is present in neutral waters as a divalent anion. Sulfate is well removed by strong base anion resins. Sulfide is well removed by strong base anion resins. Sulfite is an important reducing agent used as an oxygen scavenger in water treatment. Sulfite is well removed by strong base anion resin, however throughput capacity is generally limited by the presence of other ions that are also present.
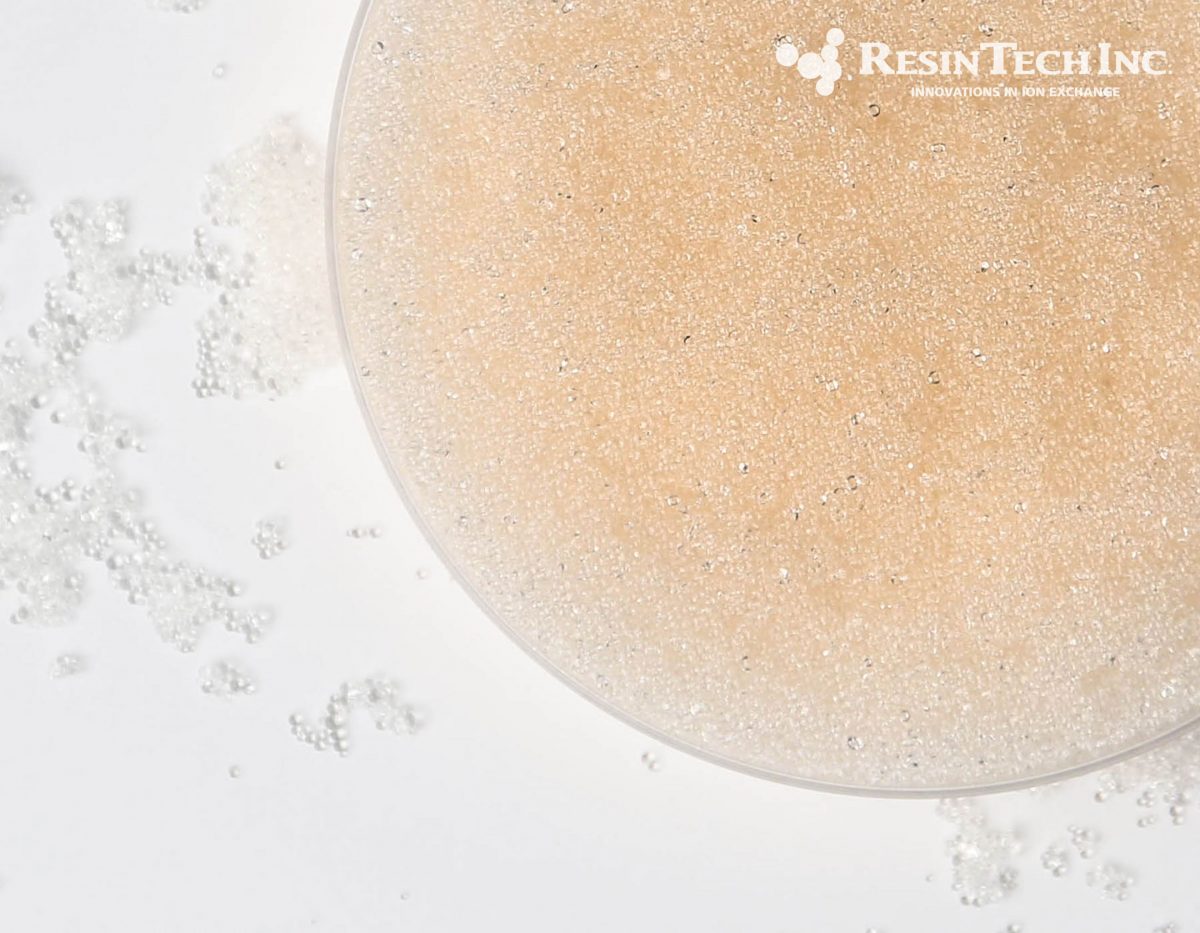
| Media Sub Category |
Strong Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Porous Gel |
| Ionic Form |
Hydroxide |
| Applications: | |
|
- Demineralization |
|
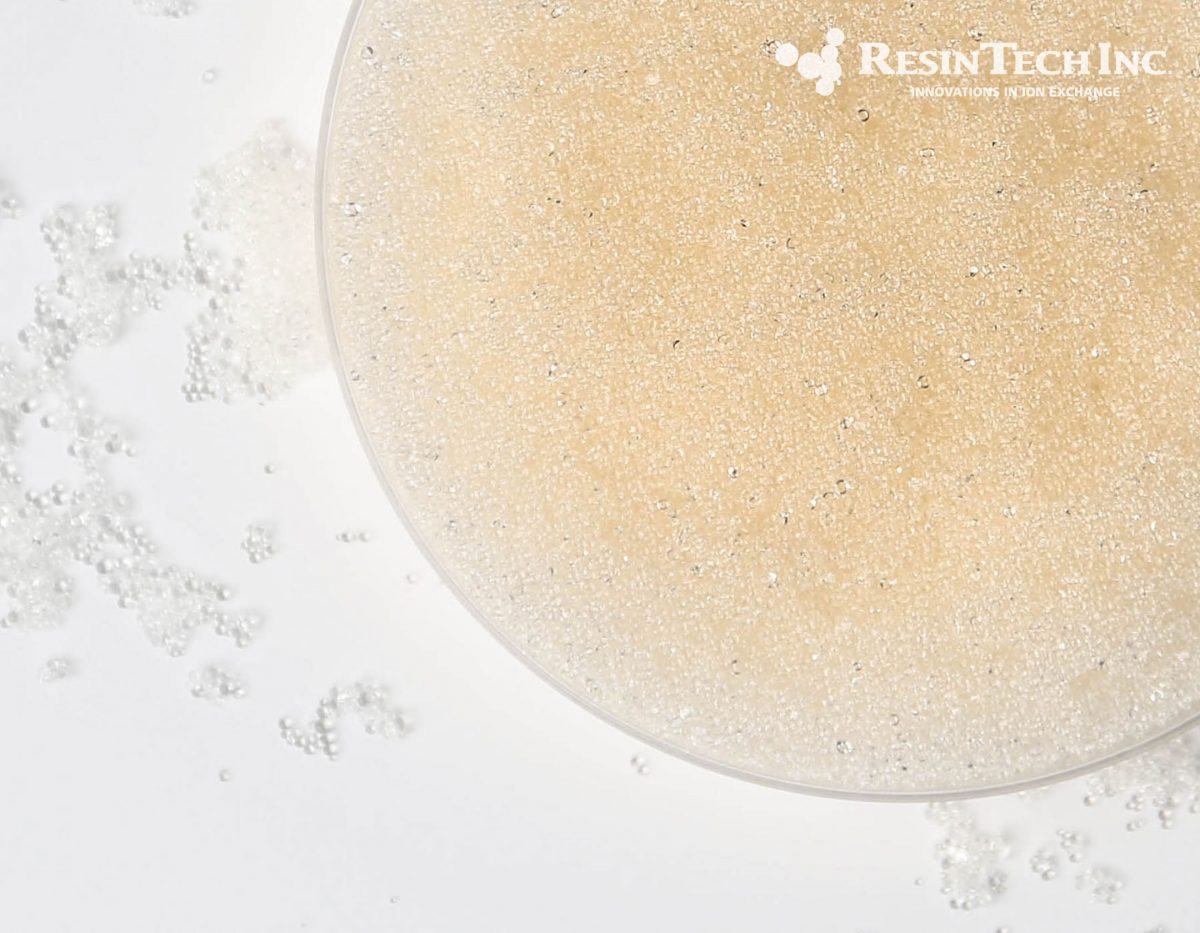
| Media Sub Category |
Strong Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Gel |
| Ionic Form |
Hydroxide |
| Applications: | |
|
- Demineralization |
|
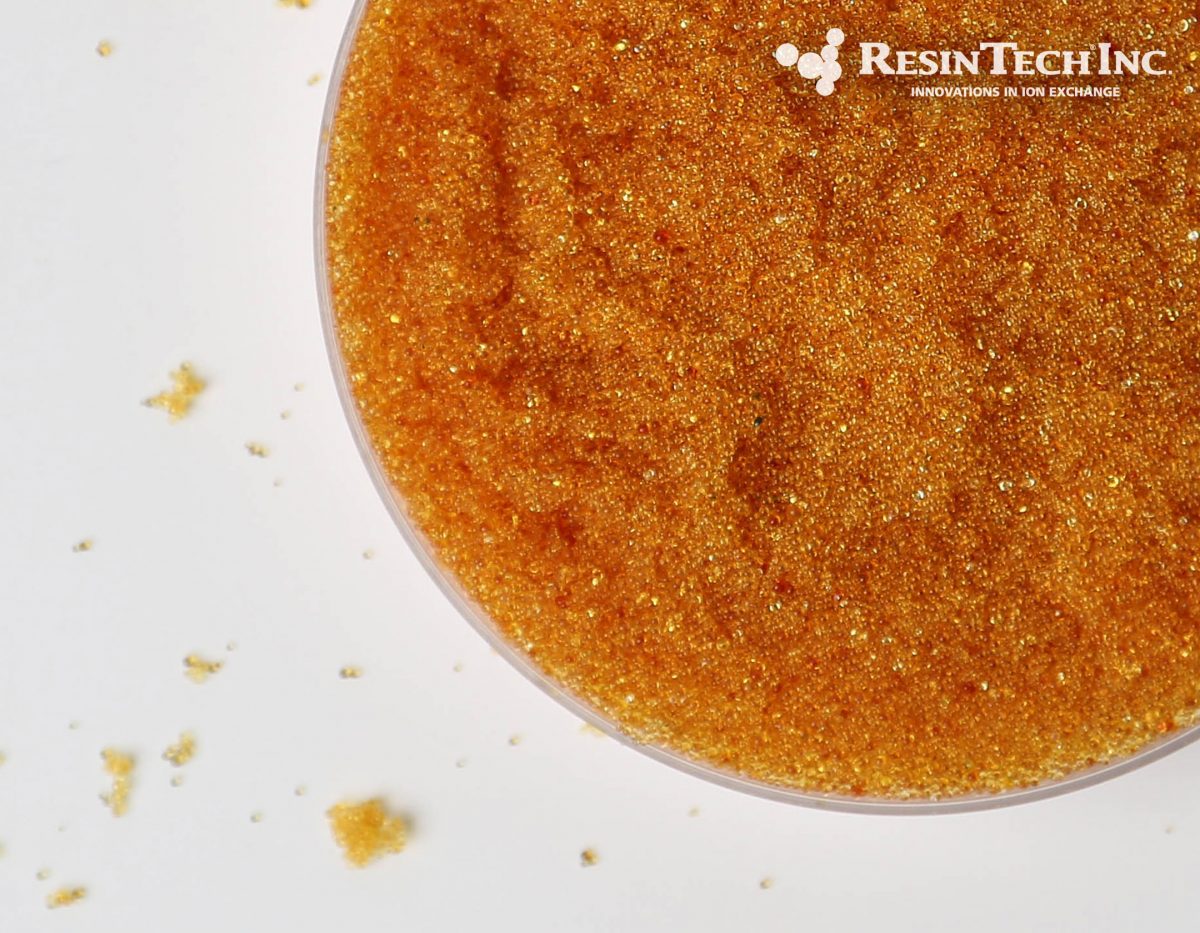

| Media Sub Category |
Strong Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Gel |
| Ionic Form |
Hydroxide |
| Applications: | |
|
- Demineralization |
|
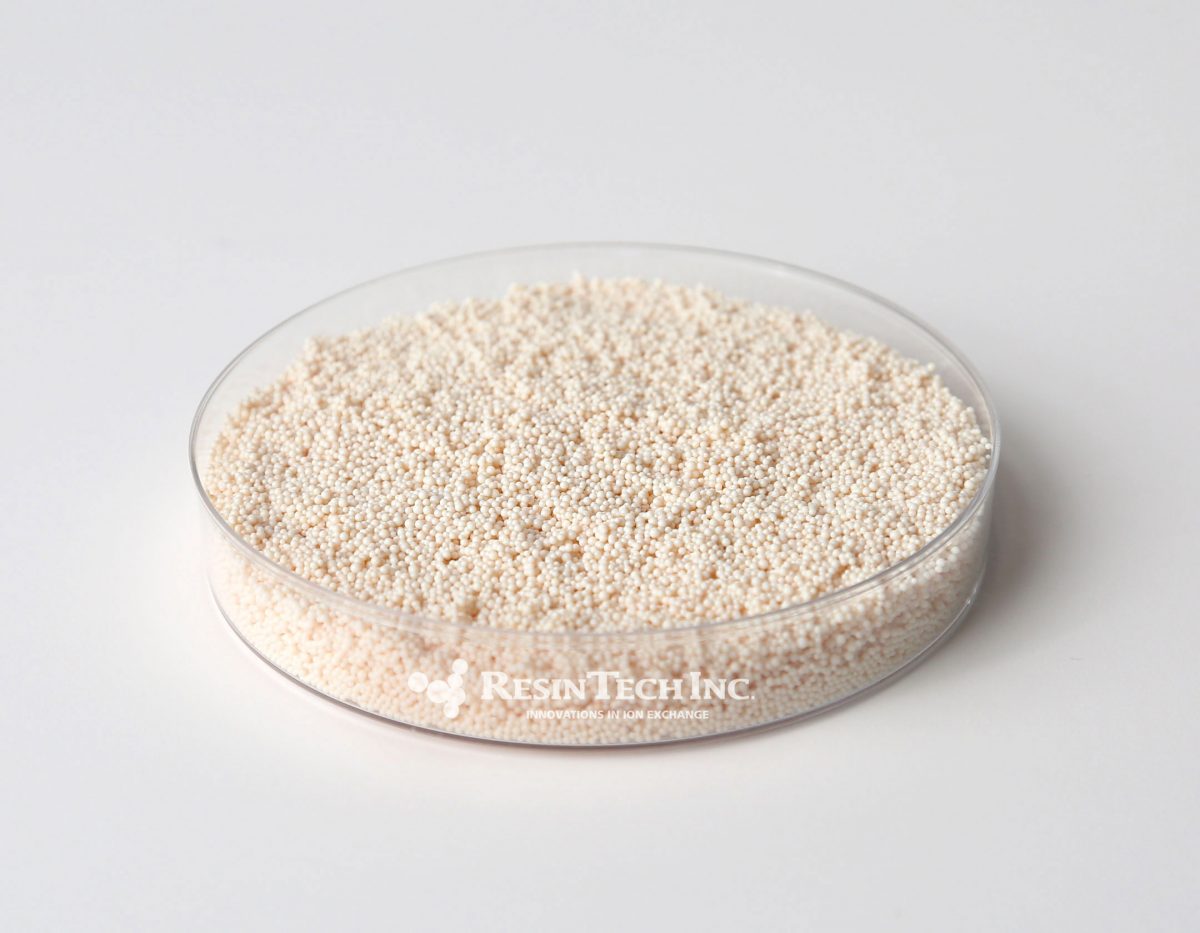

| Media Sub Category |
Weak Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Macroporous |
| Ionic Form |
Free Base |
| Applications: | |
|
- Demineralization |
|
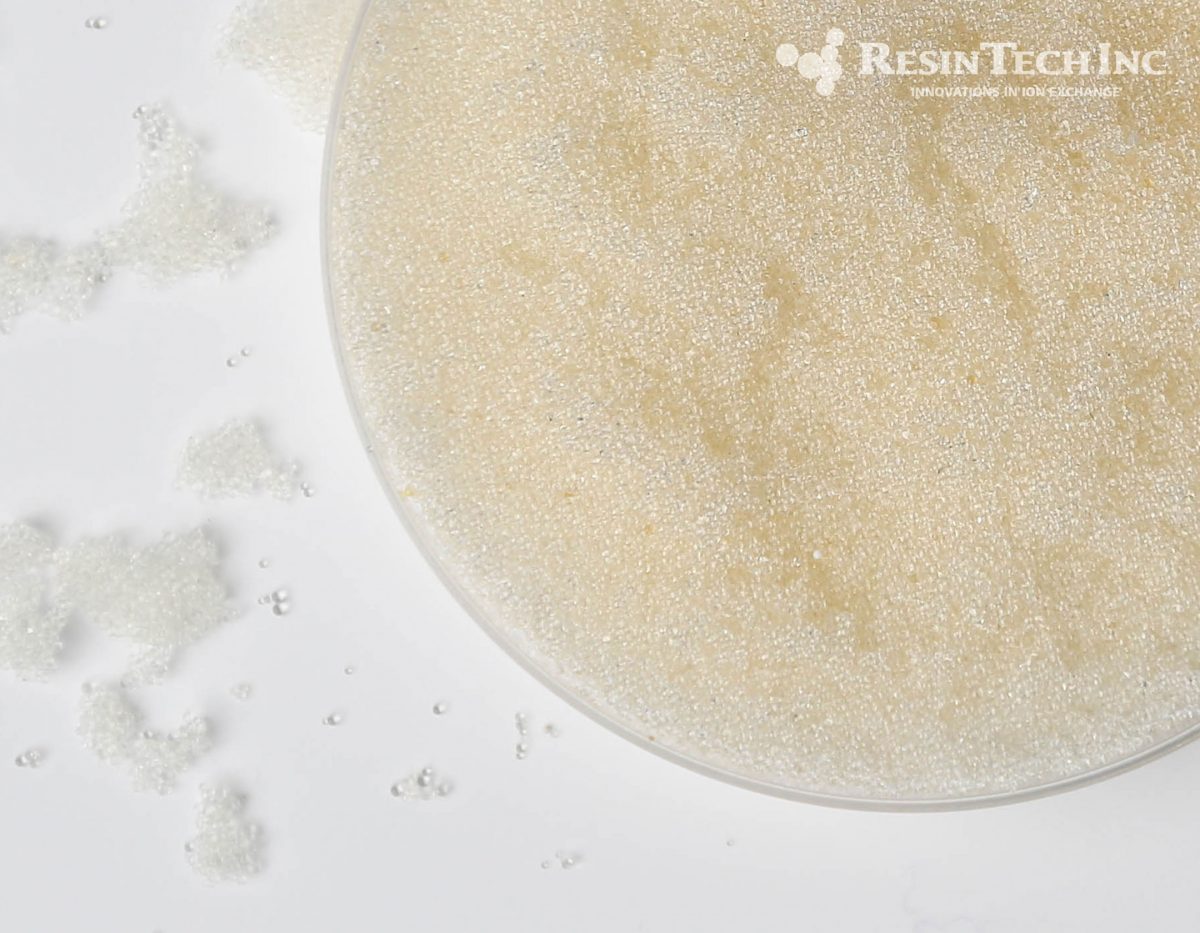

| Media Sub Category |
Strong Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Gel |
| Ionic Form |
Chloride |
| Applications: | |
|
- Demineralization |
|
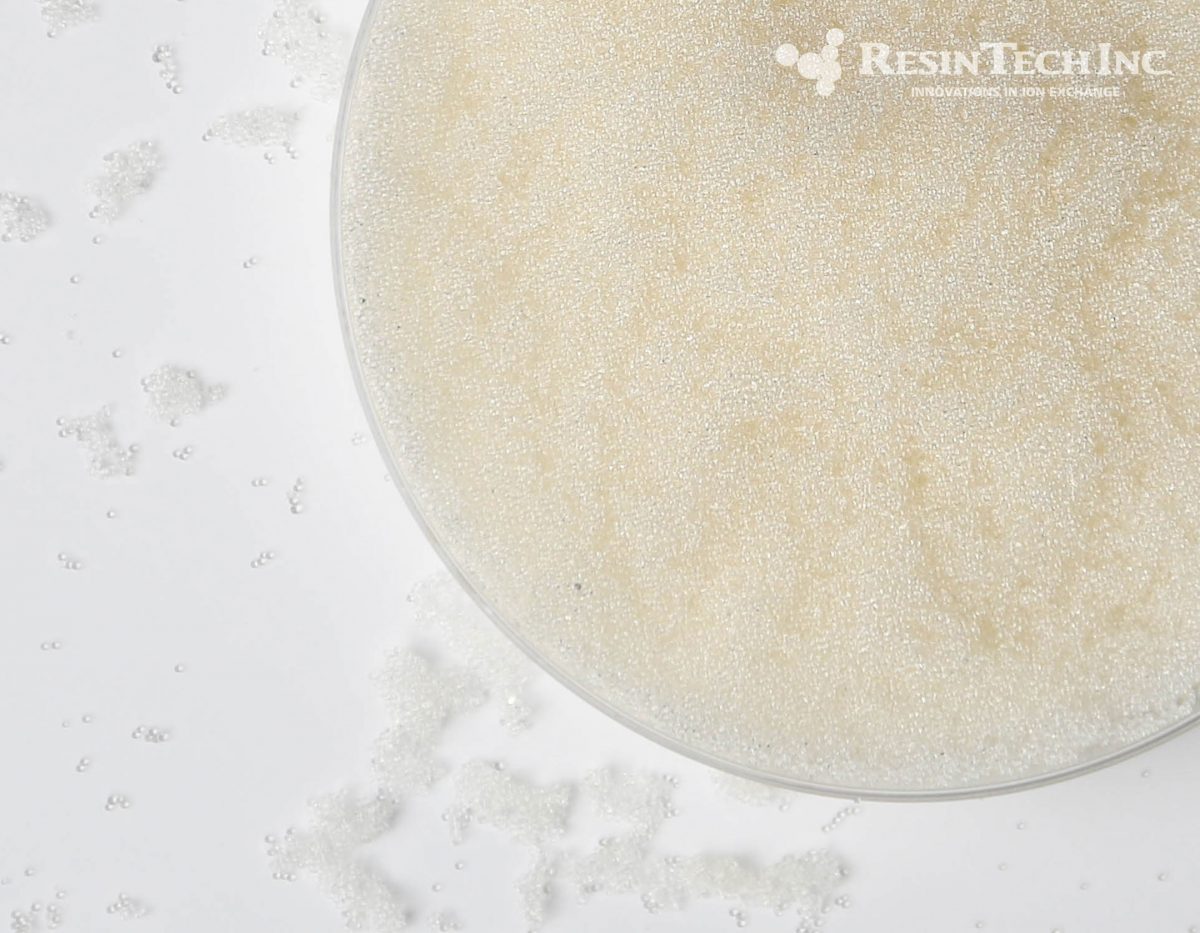

| Media Sub Category |
Strong Base Anion |
| Polymer Matrix |
Styrenic Gel |
| Ionic Form |
Chloride |
| Applications: | |
|
- Dealkalizer |
|
Need a little help deciding what to do next?
Reach out to us using the link below.
Tel: 856-768-9600
Fax: 856-768-9601
©2024 ResinTech, Inc.